Food analysis > F-6P fibre extractor
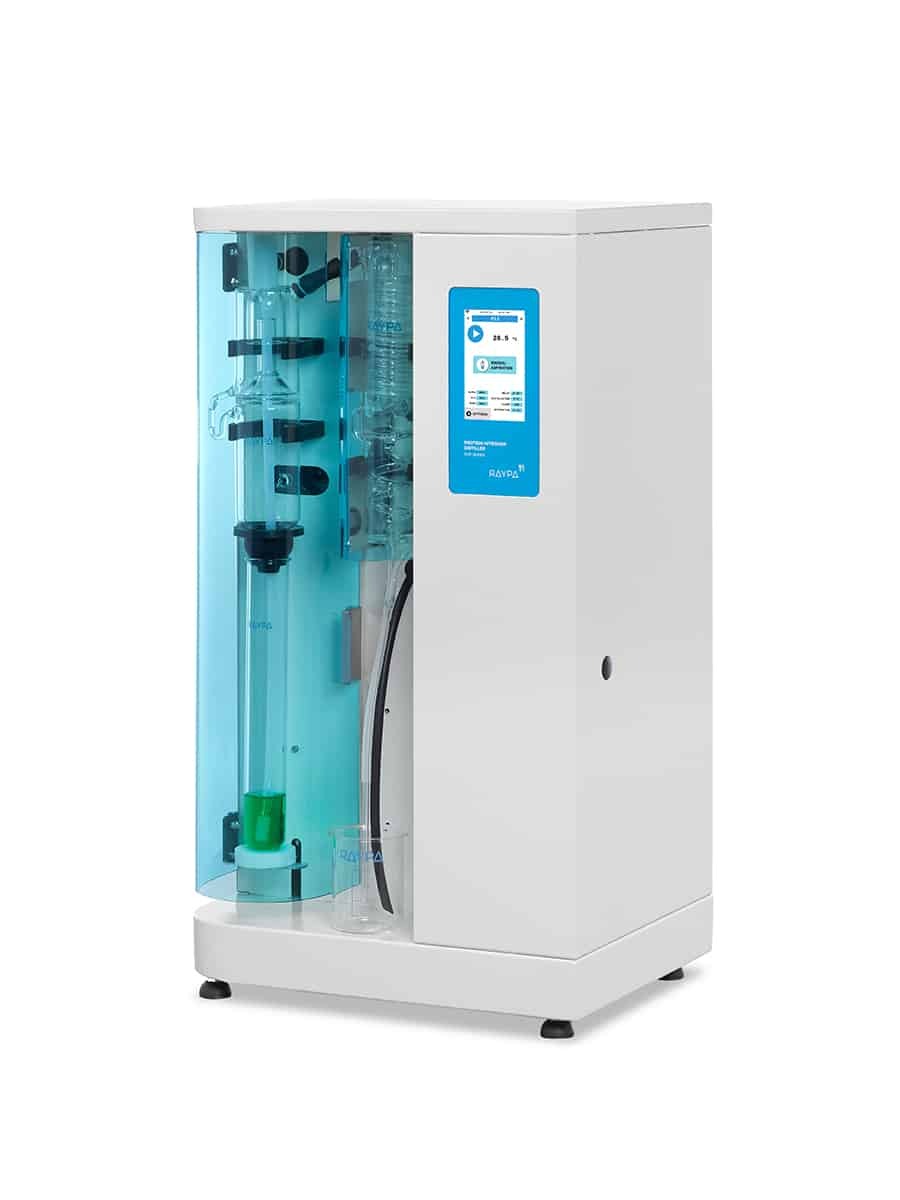
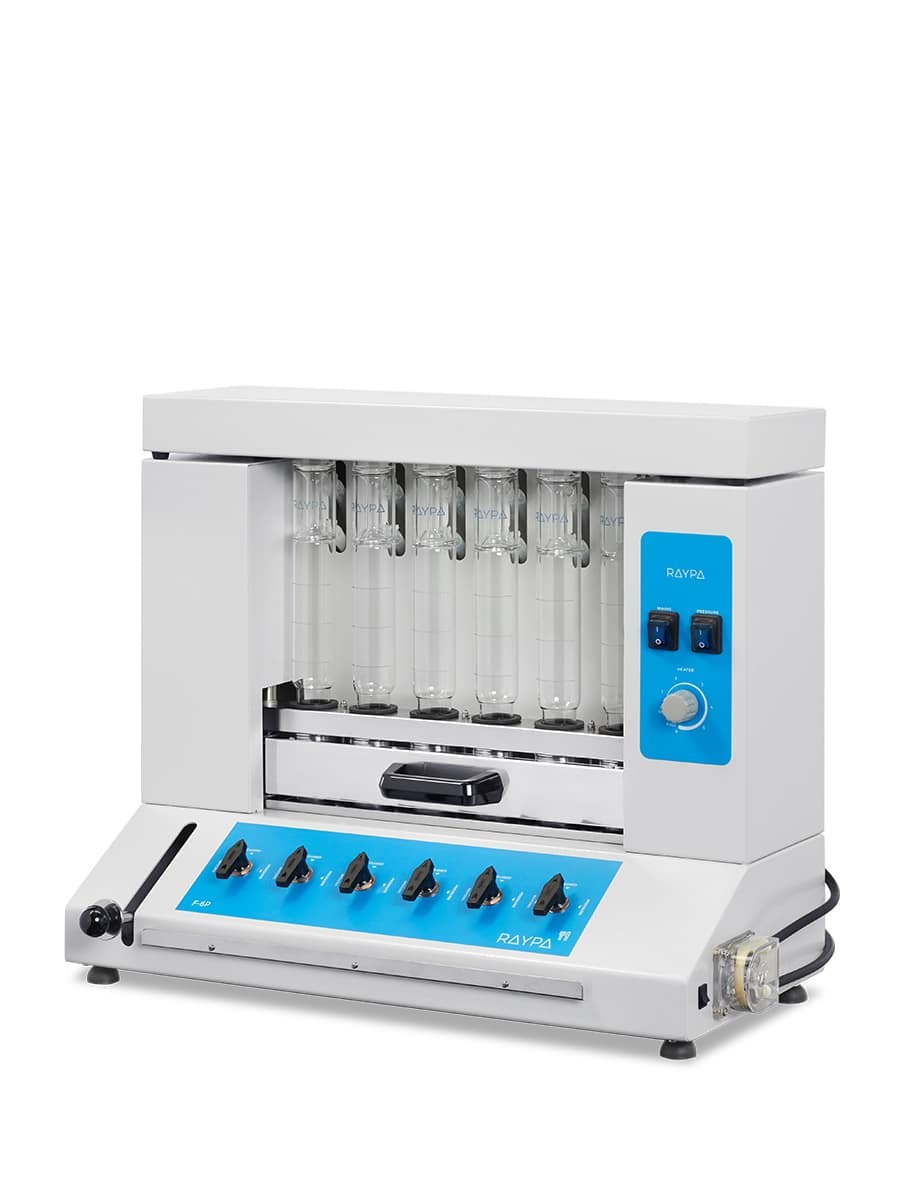
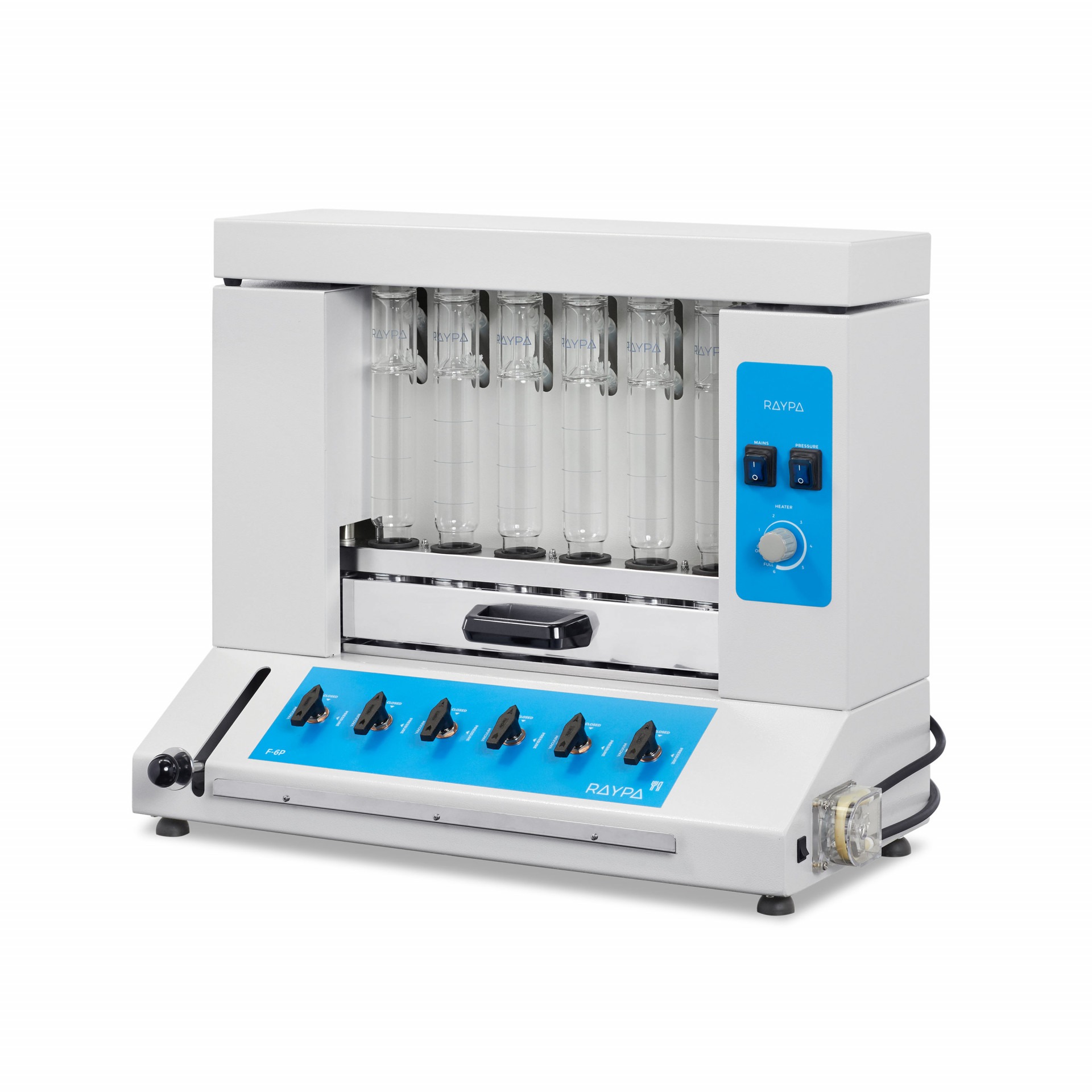
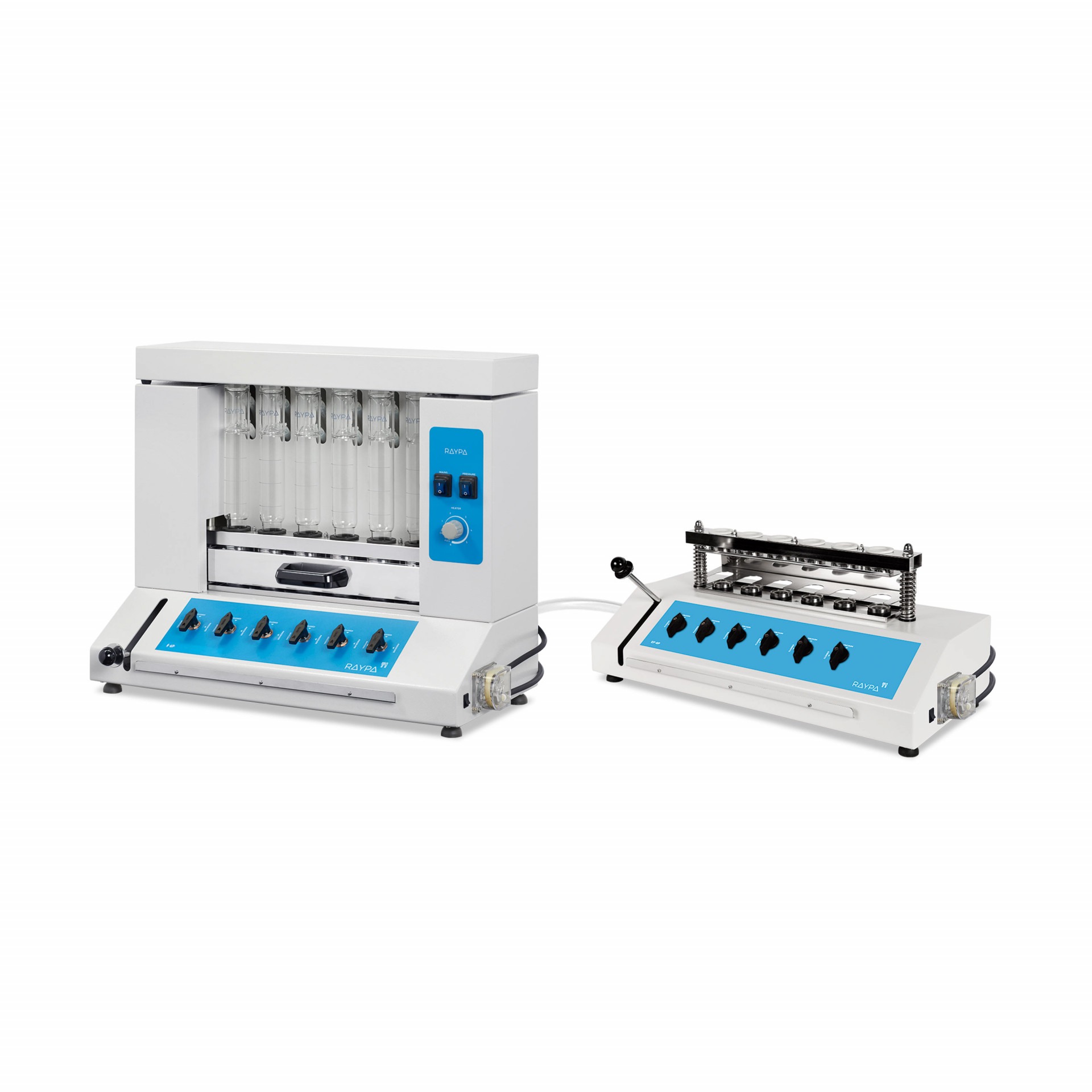
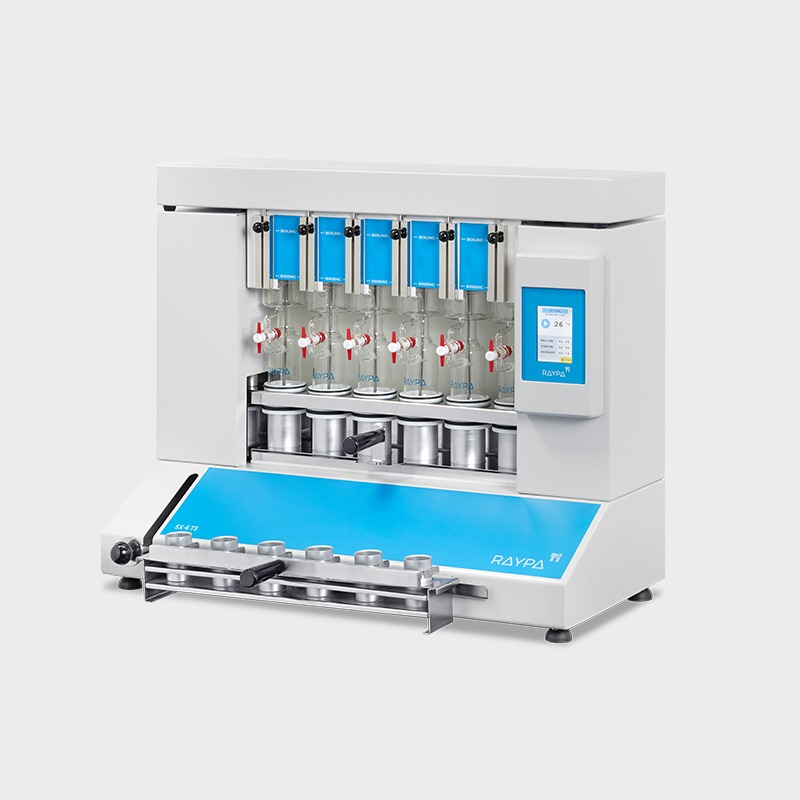
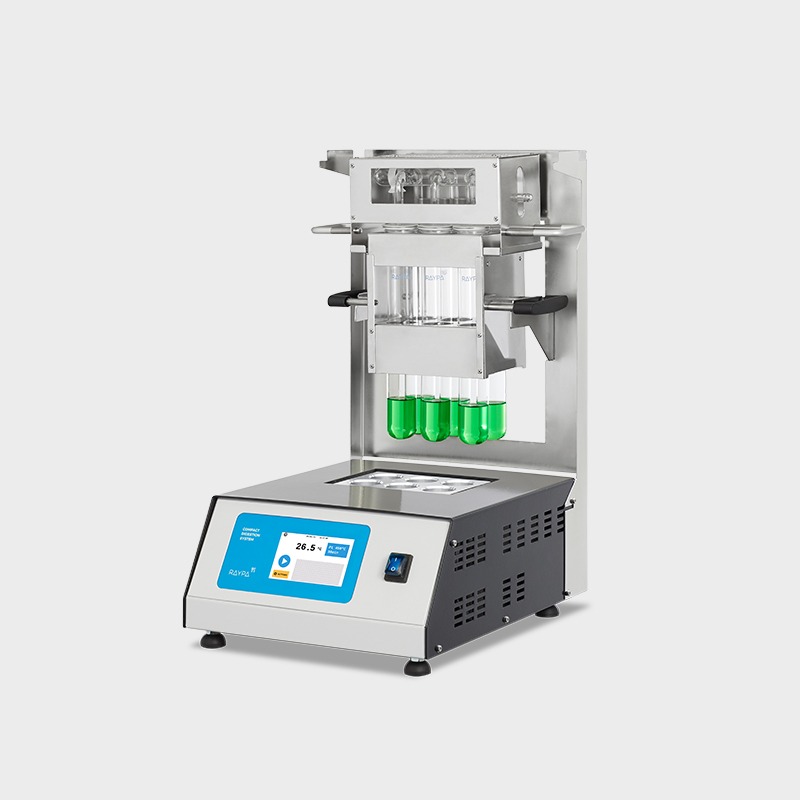
Fibre extractor
Reliable, versatile and economic fibre extraction system for efficient analyses of crude fibre and fractions of detergent fibre.
- Faster extractions thanks to air compressor and peristaltic pump
- In accordance with the official Weende and Van Soest methods
- Extraction and filtration without sample transfer
Hot extraction system according to the Weende and Van Soest methods
Our fibre extractor has been specifically optimized for the determination of crude, acid, and neutral fibre along with other fractions such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin according to the universally recognized official Weende and Van Soest methods.
Its flexibility to analyze a wide range of samples with subsequent or individual extraction, including boiling and filtration steps, makes our hot fibre extractor suitable for multiple applications. Its design ensures accurate and precise results in accordance with international standards AOAC, AACC, and ISO.
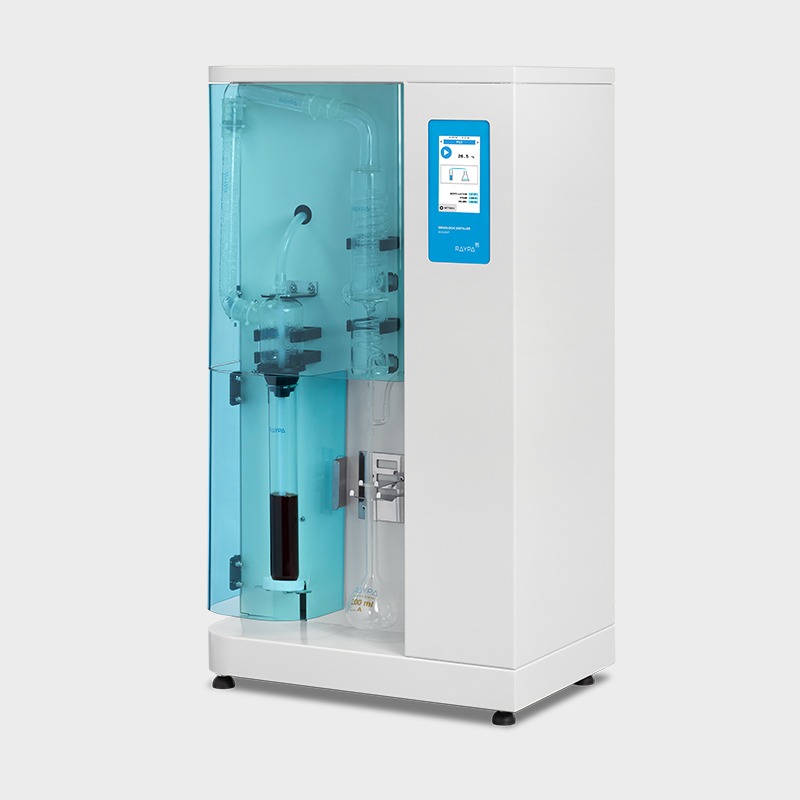
The main compatible applications include the determination of crude fibre content according to the Weende method, as well as measuring acid detergent fibre (ADF) and neutral detergent fibre (NDF) following the Van Soest method, along with acid detergent lignin (ADL) analysis. Use in conjunction with the EF-6P Cold fat extractor allows for a comprehensive solution to pre-degrease samples with high fat content and also extract organic solutes.
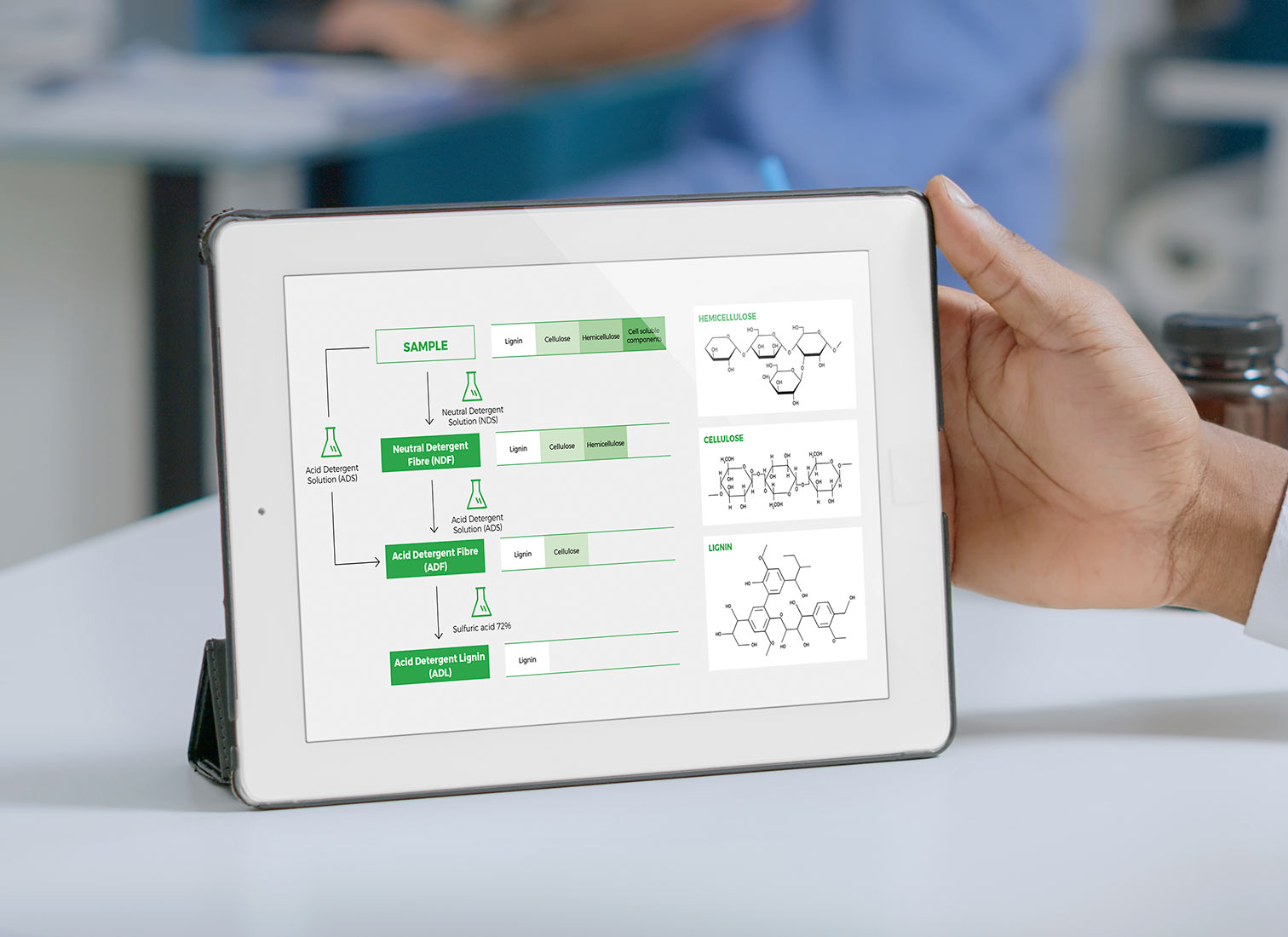
DETERMINATION OF MULTIPLE FIBRE FRACTIONS
The fibre extractor is an essential tool for the determination of crude fibre, known as the non-digestible residue, offering rapid analysis, reliable results, and high reproducibility. Its ideal applications include the Weende method, the oldest analytical procedure in use, where the concentration of fibres is measured as Crude Fibre (CF); Neutral Detergent Fibre (NDF), a common method in animal feed analysis; Acid Detergent Fibre (ADF), which includes cellulose, lignin, and xylans; and the determination of Acid Detergent Lignin (ADL) and Wijkstrom's technique, a modification of the Weende method.
VERSATILITY FOR A DIVERSE RANGE OF SAMPLES
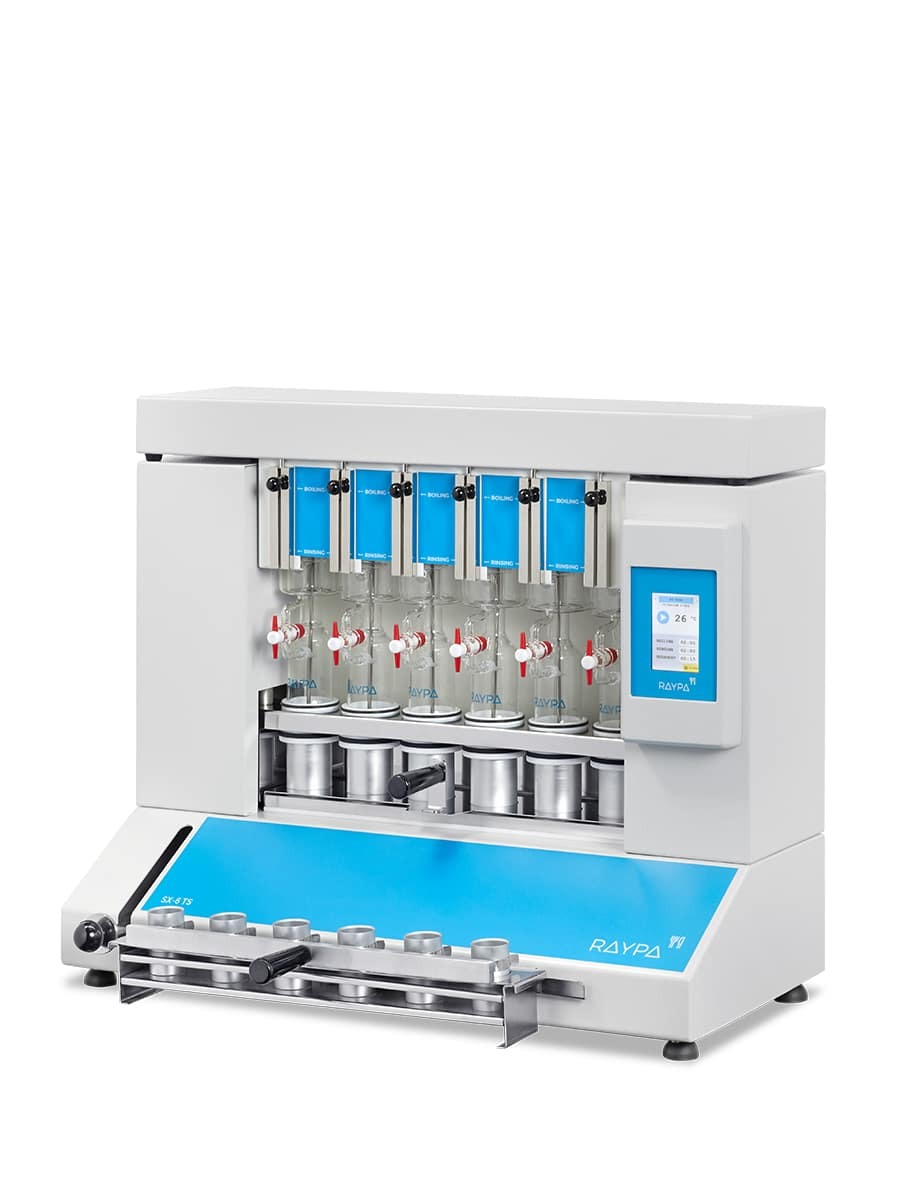
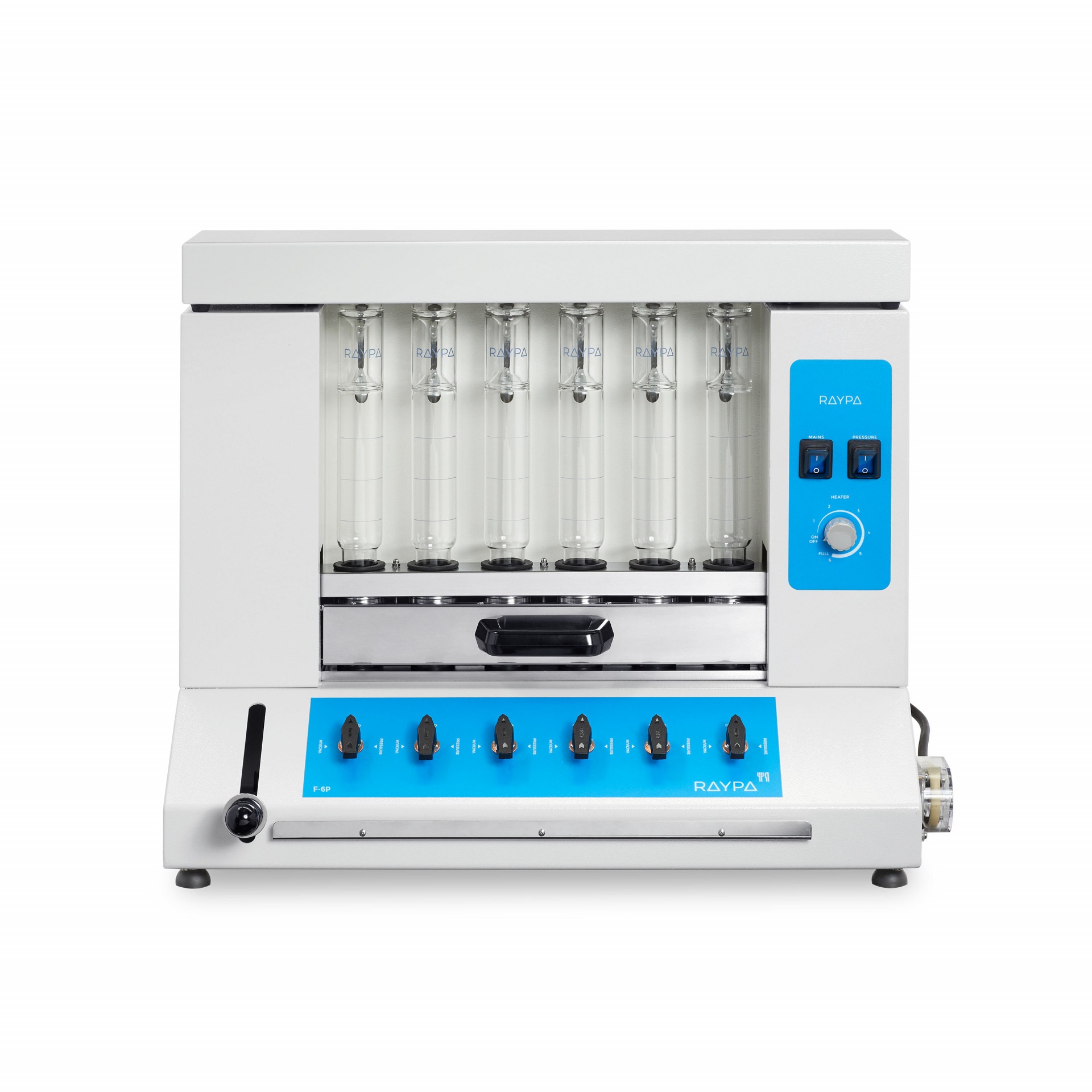
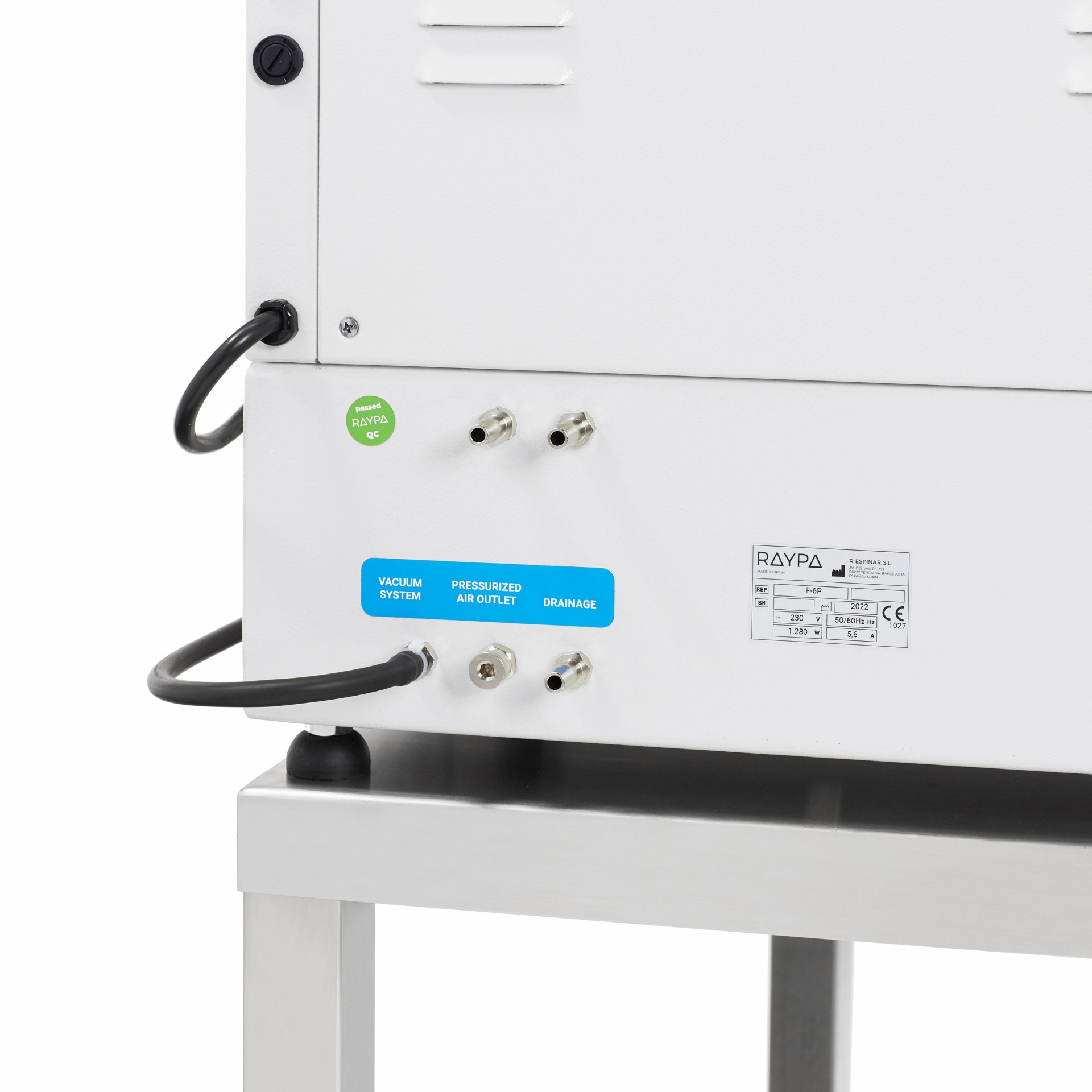
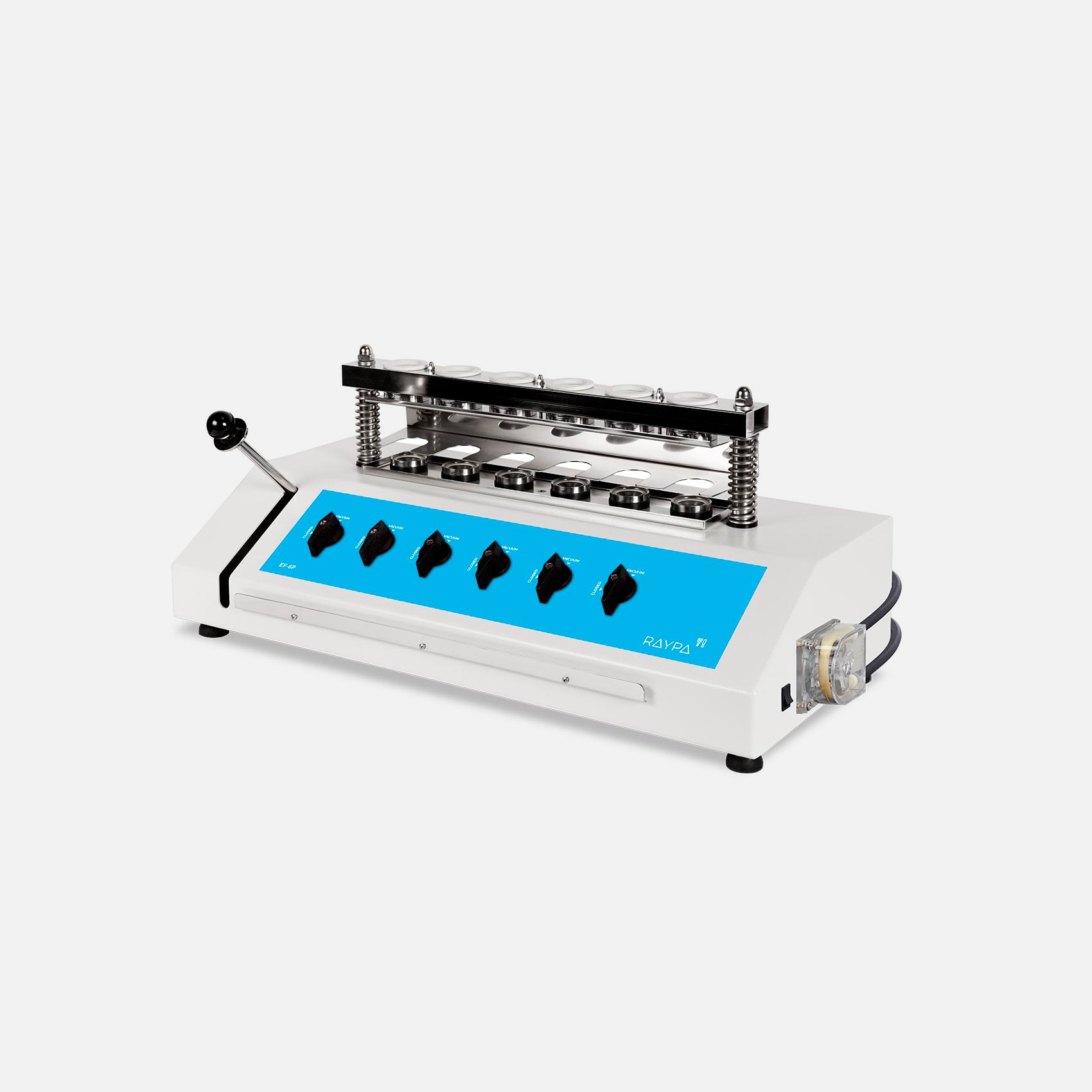
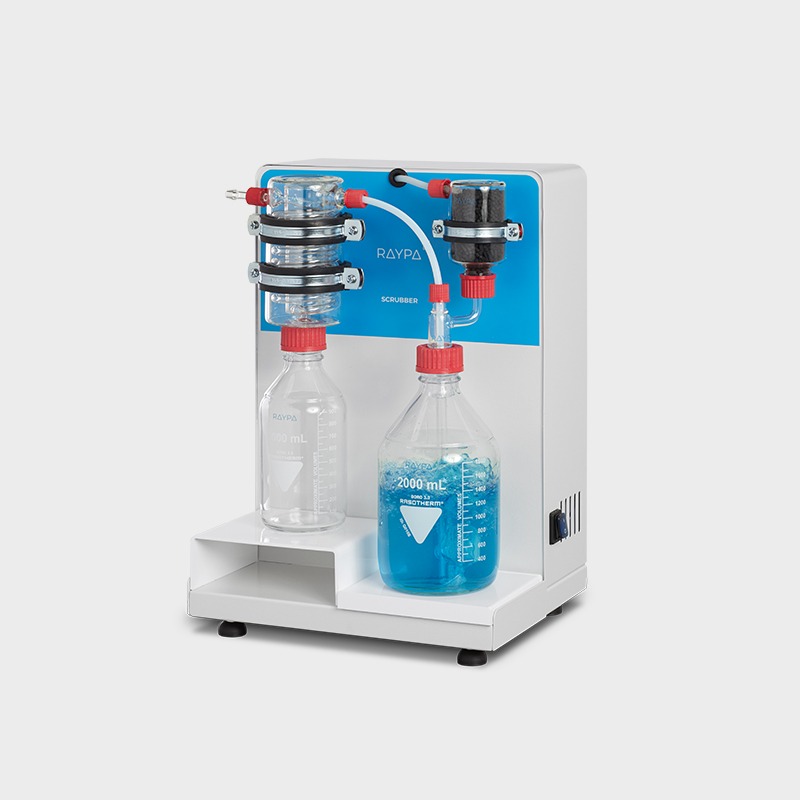
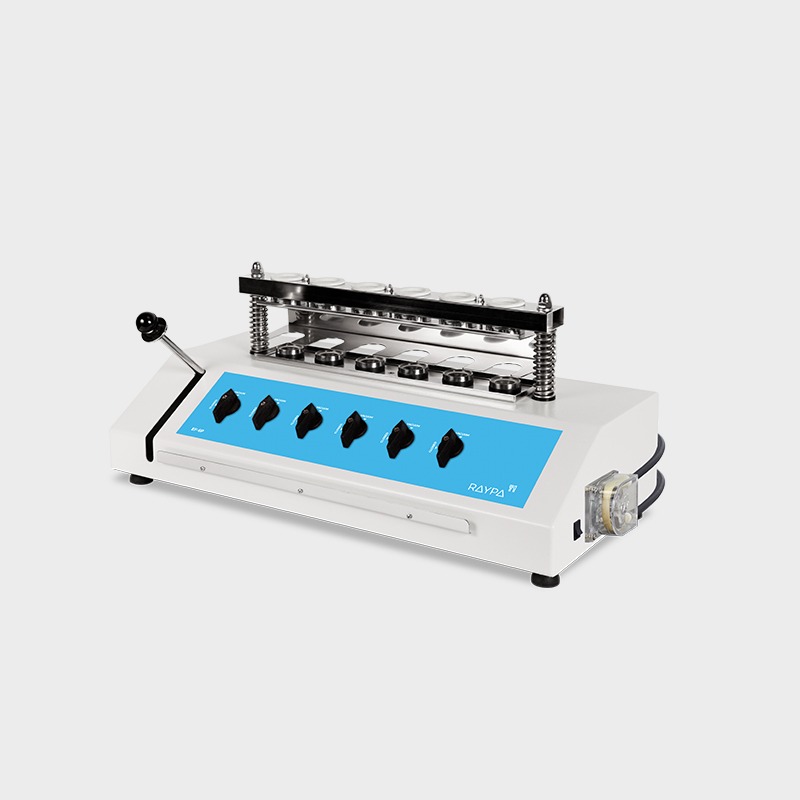
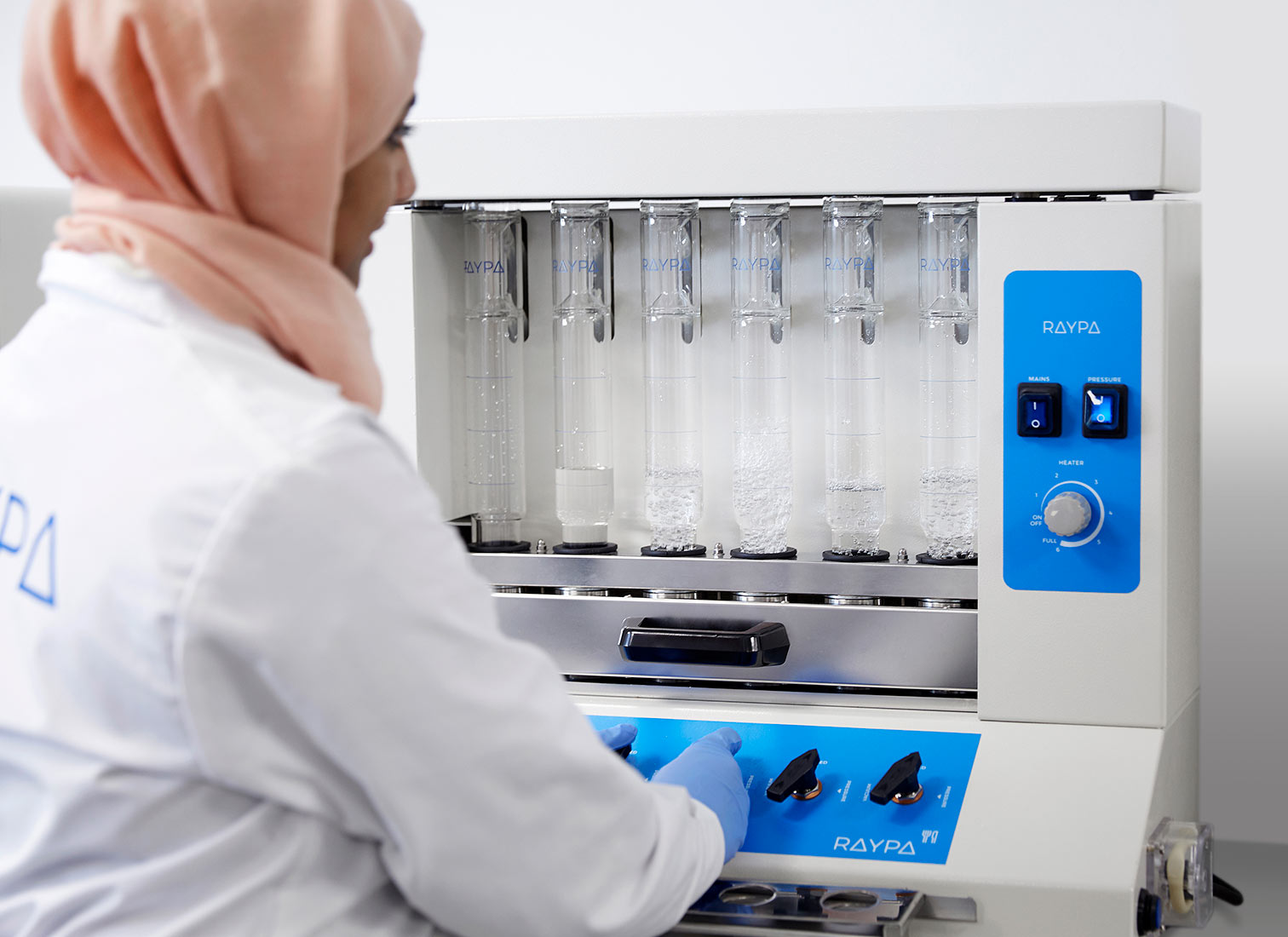
Hot extraction of 6 samples simultaneously or sequentially under identical conditions, including boiling and filtration. Extraction and filtration without sample transfer. Samples can be dried and weighed at each extraction stage. Control of the extraction steps via 3-position valves (closed, drainage, and positive pressure). The integrated air compressor provides positive pressure support to break up clumps during filtration, and the vacuum pump provides negative pressure support to speed up the extraction.


SUPERIOR CONSTRUCTION QUALITY WITH A FOCUS ON SAFETY AS A TOP PRIORITY
Main structure made of stainless steel painted with epoxy resin for exceptional strength and durability. It has 6 individually adjustable simultaneous extraction positions. Includes solvent recovery tanks, all necessary components for safe sample handling and a set of 12 Viton® and EPDM gaskets. The system also has a specific screen for technical personnel and an access port for inserting an external validation probe. If an error is detected, the display will show an alert message allowing for quick correction of the problem.
Operation
HOT EXTRACTION FOR THE DETERMINATION OF CRUDE FIBRE AND DETERGENT FIBRE
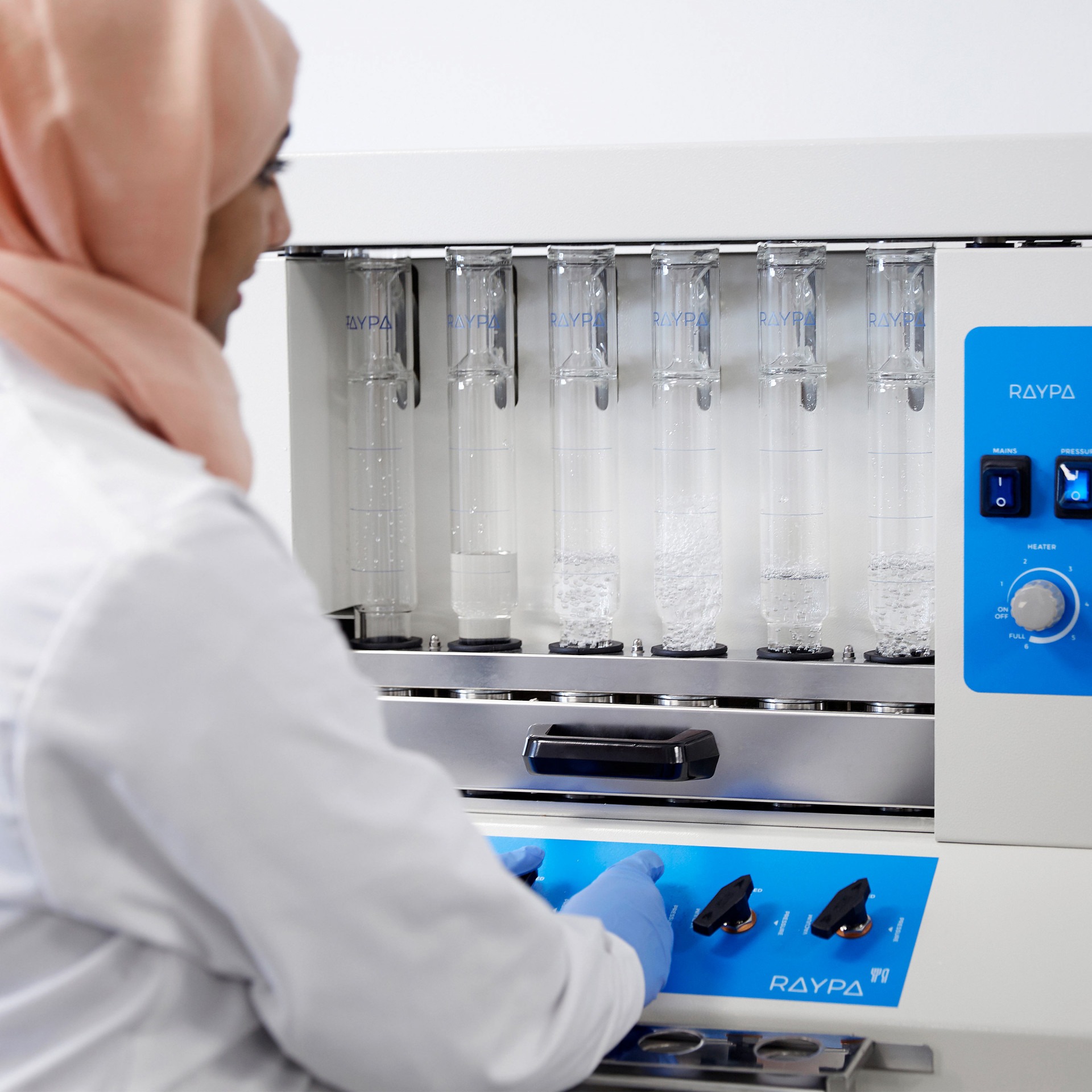
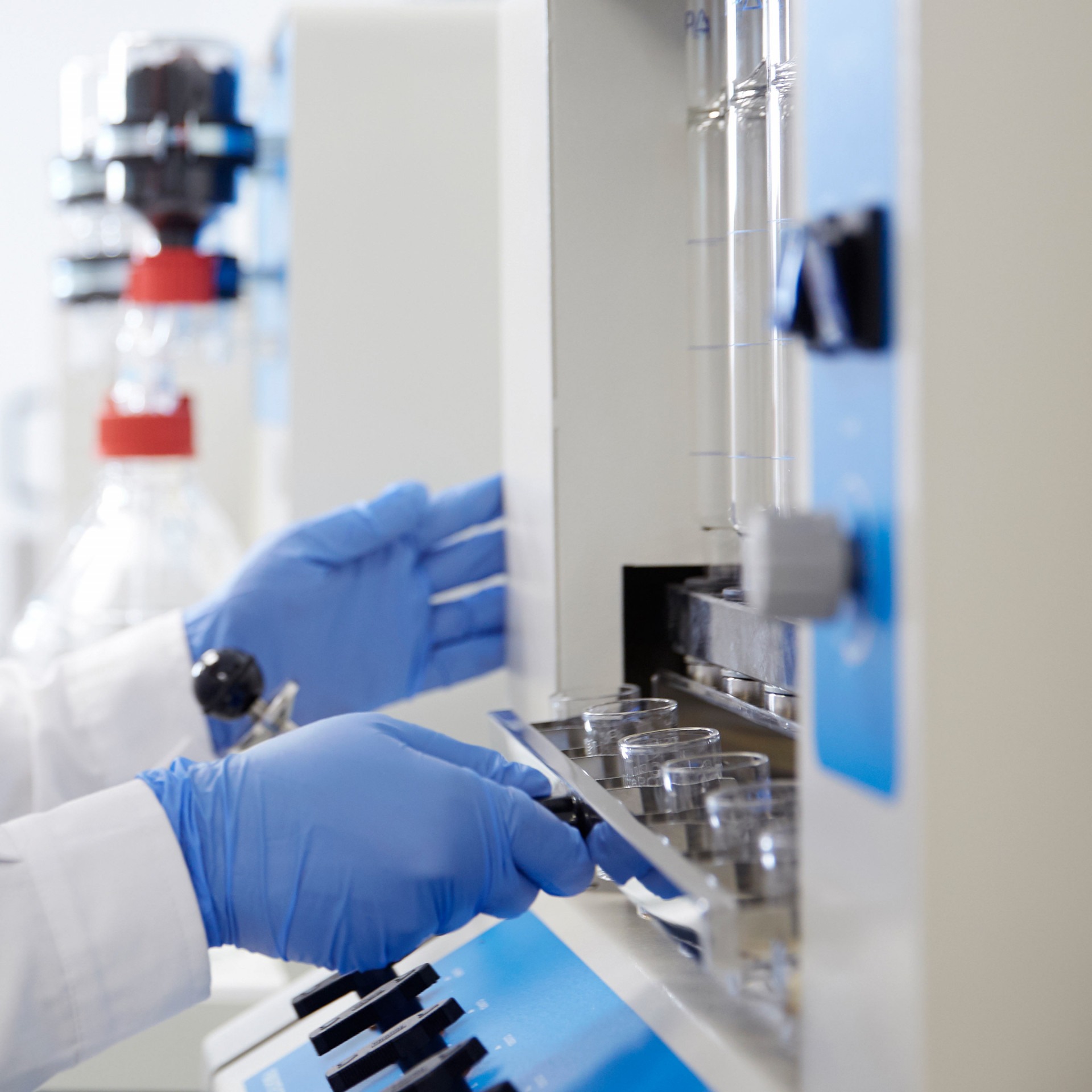
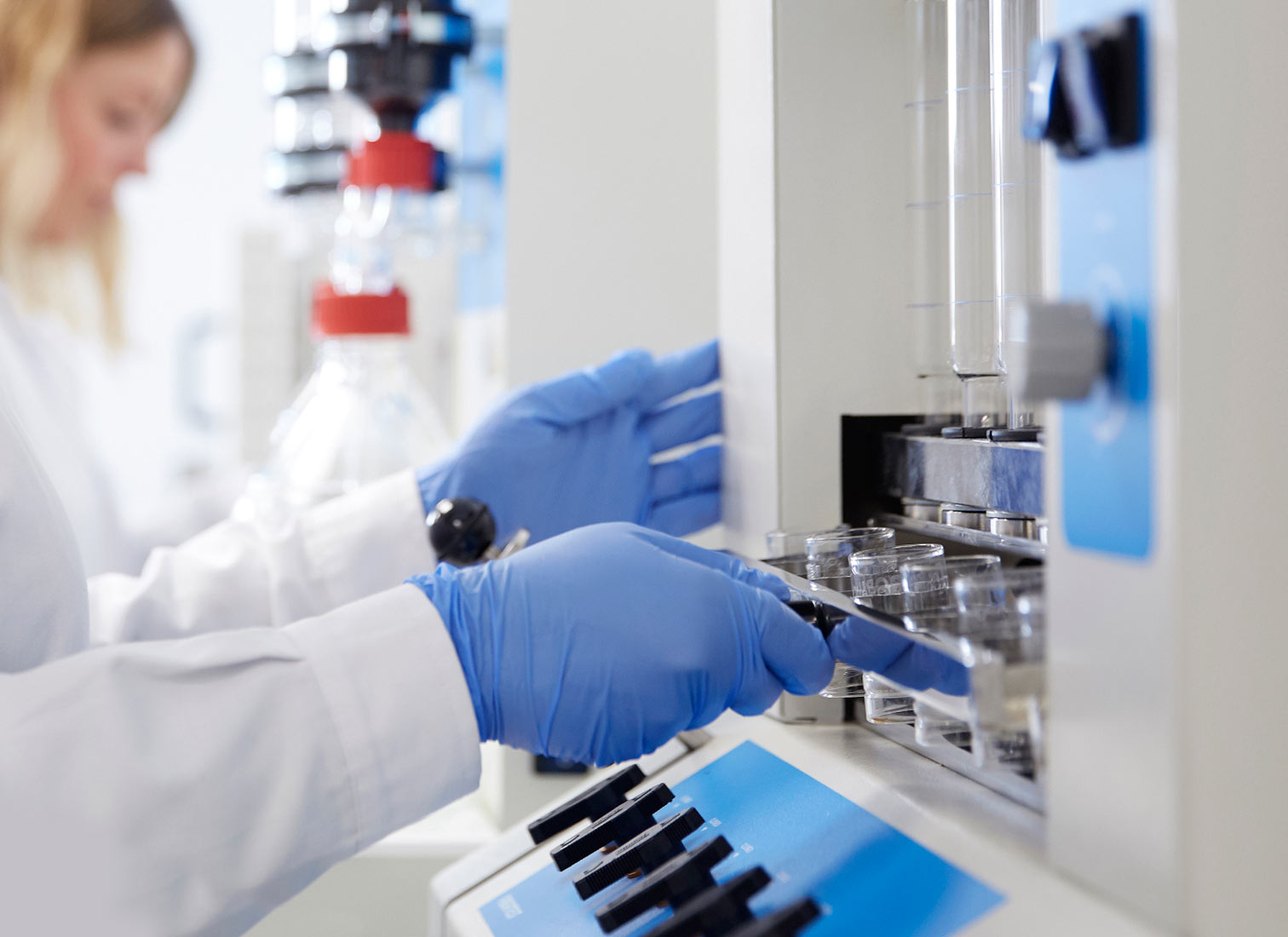
The hot extraction method for the analysis of crude fibre and detergent fibre aims to separate the harder-to-digest fractions (hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin) from the more digestible ones (starch and sugars) using various solvents and detergents. This extraction technique, conducted in a fibre extractor, offers more efficient and accurate recovery and analysis. Thanks to the capability to expedite and meticulously monitor each phase of the process without sample transfer, laboratories equipped with our fibre extractor can ensure consistent quality with reliable results.
For Neutral Detergent Fibre (NDF) analysis, the process begins with sample preparation. Each sample is carefully weighed and placed in a crucible of known porosity, designed to withstand the necessary temperatures during hot extraction. In the first phase, the digestion phase, the sample is boiled in continuous contact with the Neutral Detergent Solution (NDS) containing heat-resistant alpha-amylase, which helps to separate the neutral detergent soluble fraction (sugars, starches, and soluble pectins) from the neutral detergent insoluble fraction (cell wall components, hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin). Optionally, to expedite the process, the fibre extractor’s air compressor can be activated to break down compacted lumps in the crucible’s filter. Then, in the washing phase, the residue in the crucibles is washed with water to remove any detergent residues. Finally, in the degreasing phase, a wash with acetone is performed. Upon finalization, the fibre fraction under examination resides at the bottom of the crucible, ready for subsequent quantification and analysis of the neutral fibre fraction.
Applications
Technical data
| Reference |
|---|
| Sample positions |
| Dimensions of glass crucible (Ø x H mm) |
| External dimensions (L x D x H mm) |
| Net weight (Kg) |
| Power (W) |
| Voltage* (V) |
| Frequency (Hz) |
| *Other voltages and electrical configurations available on request. |