Flash sterilization
Discover how the flash cycle in autoclaves offers a fast and effective instrument sterilization in emergency situations. Read the full article for detailed information and applicable contexts.
The flash sterilization cycle is a fast and effective sterilization method widely used in emergency situations in various sectors such as healthcare and microbiology. This procedure is conducted in steam autoclaves and is essential for scenarios requiring the rapid processing of solid objects for immediate application.
What is flash sterilization?
Flash sterilization is a specialized cycle for autoclaves equipped with steam generators, vacuum systems, and final drying mechanisms. This process necessitates the use of high-quality steam and systems designed to eliminate any cold air pockets. The process is divided into the following stages:
Stages of the flash sterilization cycle
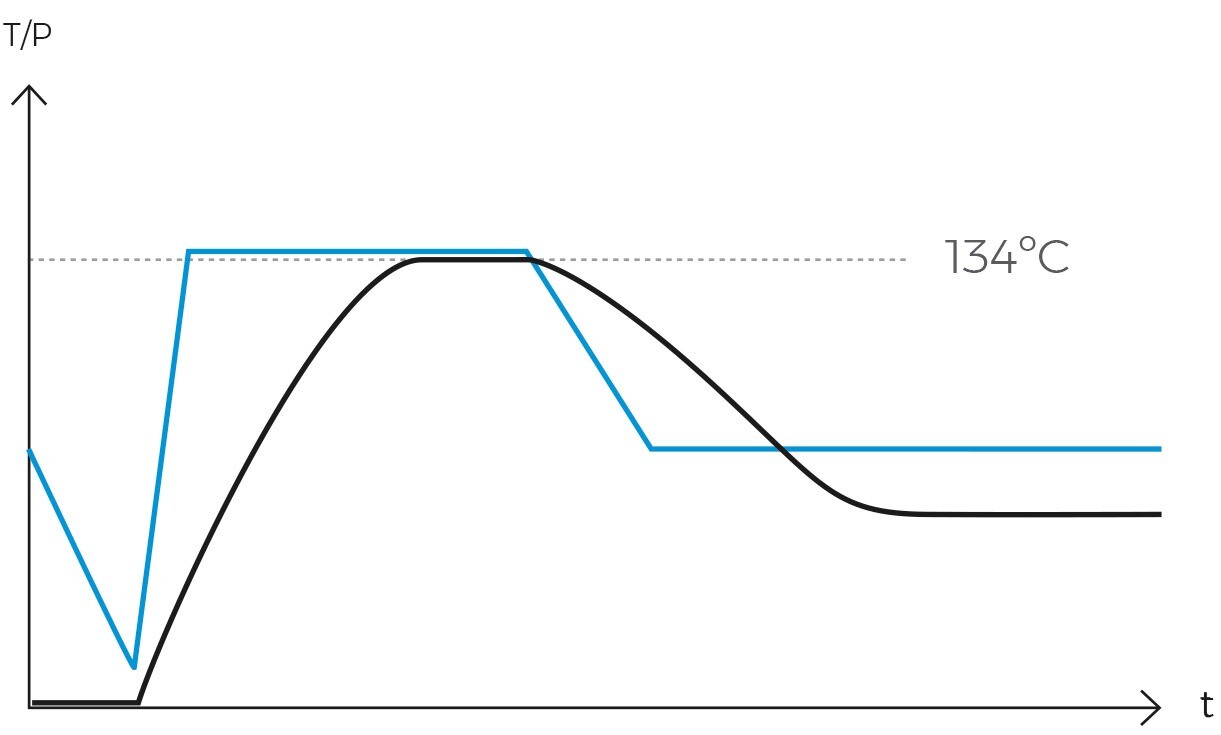
-
Purge or air removal phase
It is essential to expel all air from the chamber to ensure that steam can penetrate all surfaces of the load. In the flash cycle, a single vacuum pulse is employed to save time.
-
Heating phase
Following the purging phase, the autoclave injects high-temperature steam into the chamber until the sterilization temperature is reached.
-
Sterilization phase
This stage is shorter in duration compared to a standard cycle due to the use of a sterilization temperature exceeding 130ºC.
-
Drying phase
After the sterilization phase, the autoclave initiates the drying phase. Typically, this process involves a heating jacket that raises the temperature of the chamber walls and the objects inside, while a vacuum pump expels all moisture to the exterior. By the end of this stage, the load will be completely dry.
Importance of flash sterilization
Flash sterilization is crucial in emergency situations or when a rapid turnaround of instruments is required. While this procedure is used in research and microbiology settings, its significance is particularly notable in healthcare contexts. Its widespread use in these environments is due to its convenience and speed, despite being a cycle with higher failure risks compared to a standard cycle. This is because it is generally preferable to use a fractionated prevacuum consisting of multiple steam pulses rather than a single prevacuum pulse.
The popularity of the flash cycle arises from its ability to provide healthcare professionals with sterilized instruments in minimal time, thereby improving efficiency and response times in critical situations.
Key considerations and constraints in the clinical context
According to recommendations from health technology assessment agencies and regulatory authorities, the short sterilization cycle should only be employed in emergency situations where surgical instruments are urgently needed, such as in cases of accidental contamination during an operation.
Additionally, it must not be used for implantable devices due to the risk of transmitting serious infections. Nor can it be used for instruments that have been in contact with tissues at risk of transmitting prions, especially in patients with or suspected of having spongiform encephalopathy.
While flash sterilization is a viable option in certain contexts, priority should always be given to standard sterilization cycles. To avoid the necessity of flash sterilization, meticulous planning and management of surgical instruments are crucial. It is essential to anticipate and align instrument needs with the volume of scheduled interventions. For instance, maintaining an adequate number of sterilized instrument sets for each procedure helps prevent delays and reduces the need for flash sterilization in urgent situations.
Critical factors in flash sterilization
To ensure effective and safe flash sterilization, it is imperative to control and evaluate the following aspects in each rotation:
- Adequate cleaning and disinfection: Ensure proper cleaning and disinfection of materials prior to sterilization.
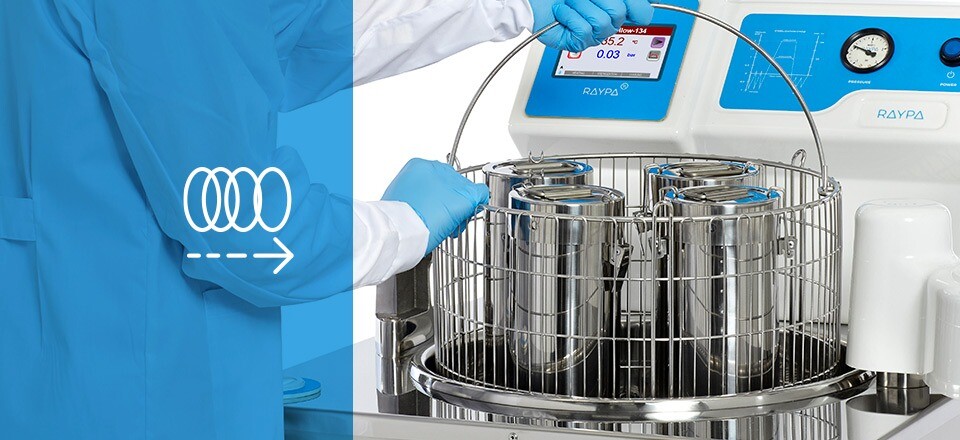
- Correct load placement: Position each item correctly to guarantee effective and even steam penetration across all surfaces of the load.
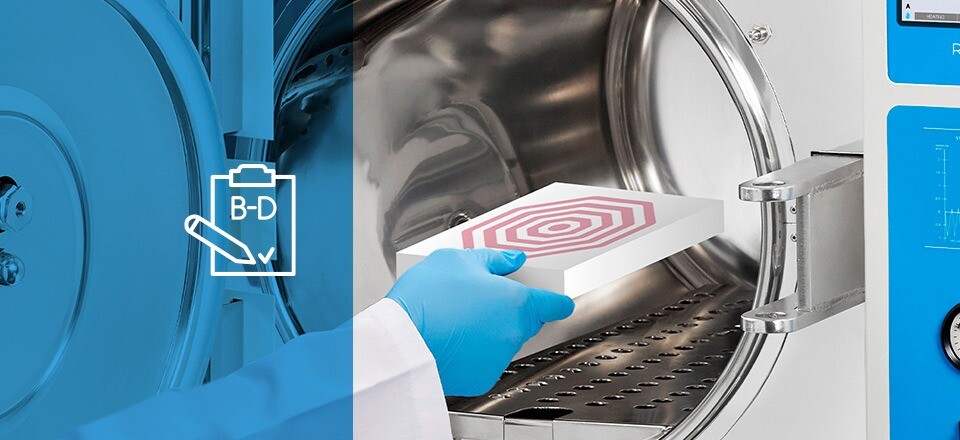
- Validation of sterilization procedures: Validate each sterilization procedure using biological and chemical indicators.
- Safe handling and transport: Ensure the safe handling and transport of materials to avoid recontamination.
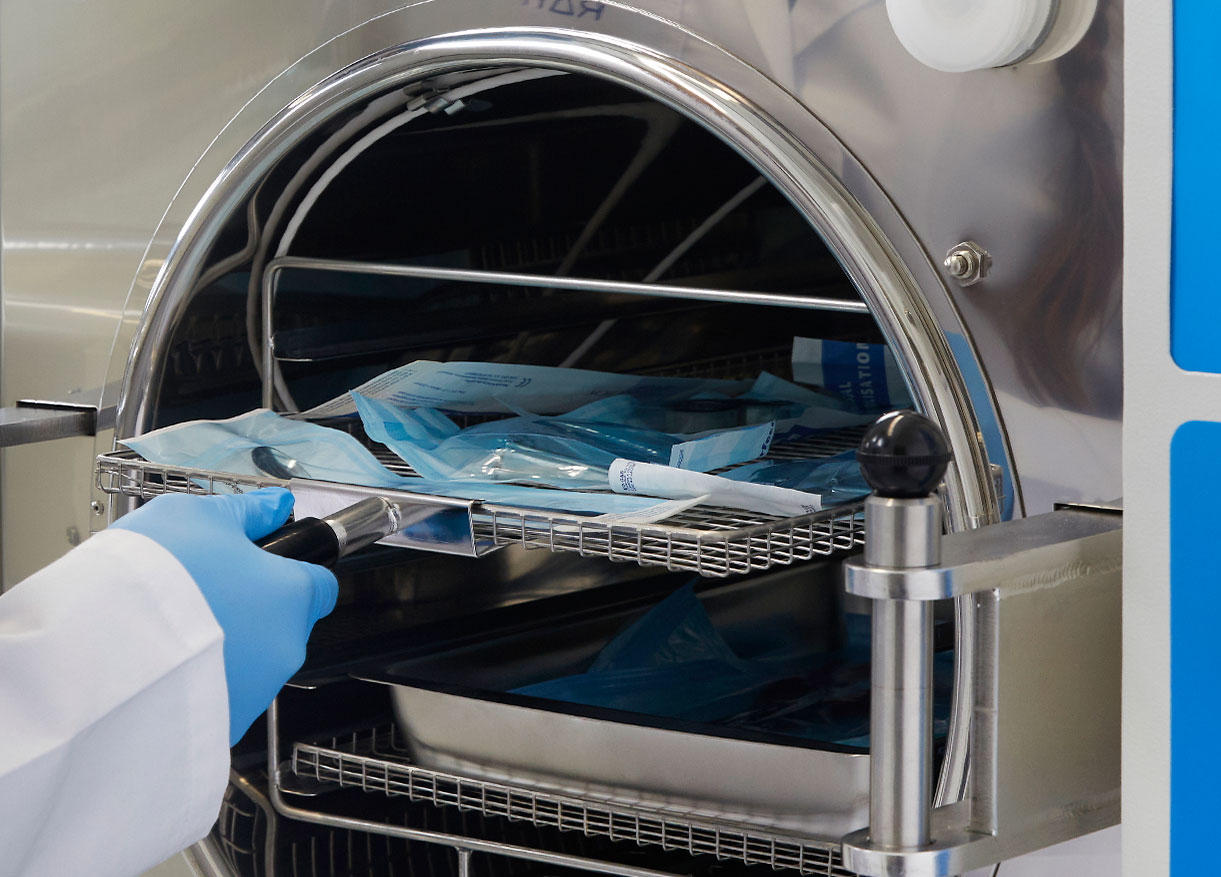

Procedures and best practices to optimize the flash sterilization cycle
To ensure the effectiveness of flash sterilization, it is essential to adhere to best practices and procedures, including:
- Proper installation of the autoclave: Ensure the autoclave is installed correctly according to manufacturer specifications.
- Regular cleaning and disinfection: Perform routine cleaning and disinfection of the autoclave chamber and its accessories.
- Comprehensive record-keeping: Maintain detailed records of all cycles performed to track usage and efficacy.
- Regular inspection and preventive maintenance: Conduct regular inspections and preventive maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This includes verifying and calibrating sensors and controls, as well as checking the condition of seals to prevent steam leaks.
- Adequate staff training: Provide thorough training for personnel on the operation and maintenance of the autoclave to ensure proper usage and safety.
Conclusions
In the clinical context, flash sterilization should be reserved for emergency situations where surgical instruments are needed immediately, and other methods are not feasible. For its proper application, it is crucial to follow strict guidelines and procedures to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the sterilization process, as the health and safety of patients are paramount.